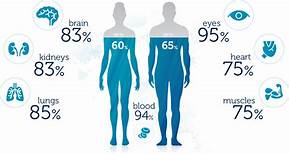
Did you know that up to 60% of the human body is made up of water. Our brain, heart, lungs, skin, kidneys etc. all contain a certain percentage of water and it is vital for our survival to keep hydrated. The loss of water and electrolytes from cells in our body is called dehydration.
Dehydration occurs in 2 ways:
- We do not consume enough fluids to offset sweat losses
- Sweat losses exceed maximum tolerable fluid ingestion e.g in warm climate (Unfortunately we don’t suffer from that in Ireland ☹)
Recommendations
It is recommended that you consume at least 2 litres of water daily. This is dependent on exercise (duration and intensity) and the temperature of the environment. This can also vary from person to person.
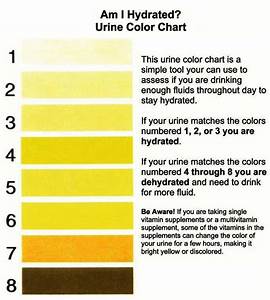
How do you know if you are dehydrated?
The colour of your urine is usually the best measure. It should be a light yellow to clear colour. If it is dark yellow/brown you are more than like dehydrated.
to edit.
Effects of dehydration on the body:
Dehydration in athletes
As athletes train frequently and deplete water stores through sweating, it is vital they are constantly hydrating. Dehydration can have a huge impact on an athlete’s performance.
Effect on performance
Hydration is vital for those who exercise and dehydration may cause problems with regards performance. Dehydration in athletes can have a huge impact on physical performance. As little as 2% can impair physical and mental performance by up to 10%.
How do we prevent this?
Hydrating pre, para and post training. At least 2 litres of water is required and
Remember dehydration is not just loss of fluids but loss of electrolytes too. A rehydration salt may be beneficial to those who find it hard to rehydrate. Some brands of electrolytes include Kinetica, ORS and Dioralite.
Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps can be seen as an effect of dehydration but they can also be as a result of neuromuscular fatigue.
Ways to avoid muscle cramps:
Next Week: Why is protein so important?
- Diarrhoea
- Headaches
- Muscle cramps
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Dry mouth, lips, eyes
Dehydration in athletes
As athletes train frequently and deplete water stores through sweating, it is vital they are constantly hydrating. Dehydration can have a huge impact on an athlete’s performance.
Effect on performance
Hydration is vital for those who exercise and dehydration may cause problems with regards performance. Dehydration in athletes can have a huge impact on physical performance. As little as 2% can impair physical and mental performance by up to 10%.
How do we prevent this?
Hydrating pre, para and post training. At least 2 litres of water is required and
Remember dehydration is not just loss of fluids but loss of electrolytes too. A rehydration salt may be beneficial to those who find it hard to rehydrate. Some brands of electrolytes include Kinetica, ORS and Dioralite.
Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps can be seen as an effect of dehydration but they can also be as a result of neuromuscular fatigue.
Ways to avoid muscle cramps:
- Keep well hydrated, not just water but also electrolytes – sodium, potassium, magnesium
- Ensure sufficient calcium in diet – calcium required for muscle contractions, lack can result in cramping
- Stretch and proper recovery
- Make sure clothes fit – tight socks, shorts, footwear can put unwanted stress on muscles
- Tonic water contains an ingredient called quinine which when consumed prior to activity may help
Next Week: Why is protein so important?

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed